Resident Crews of the International Space Station (ISS)
![]()
ISS: Expedition 72 |
 |
 |
 |
crew poster |
|
 |
 |
![]()
Crew, launch- and landing data
| No. | Nation | Surname | Given names | Position | Spacecraft (launch) |
Launch date |
Launch time |
Spacecraft (landing) |
Landing date |
Landing time |
Mission duration |
| 1 | Williams | Sunita Lyn "Suni" | ISS-CDR * | CST-100 Boe-CFT | 05.06.2024 | 14:52:15.2 UTC | SpaceX Crew-9 | 18.03.2025 | 21:57:07.14 UTC | 286d 07h 04m 59s | |
| 2 | Wilmore | Barry Eugene "Butch" | Flight Engineer | CST-100 Boe-CFT | 05.06.2024 | 14:52:15.2 UTC | SpaceX Crew-9 | 18.03.2025 | 21:57:07.14 UTC | 286d 07h 04m 59s | |
| 3 | Ovchinin | Aleksei Nikolaevich | ISS-CDR * | Soyuz MS-26 | 11.09.2024 | 16:23:12.436 UTC | Soyuz MS-26 | 20.04.2025 | 01:20:33.5 UTC | 220d 08h 57m 21s | |
| 4 | Vagner | Ivan Viktorovich | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-26 | 11.09.2024 | 16:23:12.436 UTC | Soyuz MS-26 | 20.04.2025 | 01:20:33.5 UTC | 220d 08h 57m 21s | |
| 5 | Pettit | Donald Roy | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-26 | 11.09.2024 | 16:23:12.436 UTC | Soyuz MS-26 | 20.04.2025 | 01:20:33.5 UTC | 220d 08h 57m 21s | |
| 6 | Dominick | Matthew Stuart | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | |
| 7 | Barratt | Michael Reed | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | |
| 8 | Epps | Jeanette Jo | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | |
| 9 | Grebyonkin | Aleksandr Sergeyevich | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | |
| 10 | Hague | Tyler Nicklaus "Nick" | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-9 | 28.09.2024 | 17:17:21 UTC | SpaceX Crew-9 | 18.03.2025 | 21:57:07.14 UTC | 171d 04h 39m 53s | |
| 11 | Gorbunov | Aleksandr Vladimirovich | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-9 | 28.09.2024 | 17:17:21 UTC | SpaceX Crew-9 | 18.03.2025 | 21:57:07.14 UTC | 171d 04h 39m 53s | |
| 12 | McClain | Anne Charlotte "Annimal" | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-10 | 14.03.2025 | 23:03:48 UTC | SpaceX Crew-10 | 09.08.2025 | 15:33:44 UTC | 147d 16h 29m 52s | |
| 13 | Ayers | Nichole Stilwell “Vapor” | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-10 | 14.03.2025 | 23:03:48 UTC | SpaceX Crew-10 | 09.08.2025 | 15:33:44 UTC | 147d 16h 29m 56s | |
| 14 | Onishi | Takuya | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-10 | 14.03.2025 | 23:03:48 UTC | SpaceX Crew-10 | 09.08.2025 | 15:33:44 UTC | 147d 16h 29m 56s | |
| 15 | Peskov | Kirill Aleksandrovich | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-10 | 14.03.2025 | 23:03:48 UTC | SpaceX Crew-10 | 09.08.2025 | 15:33:44 UTC | 147d 16h 29m 56s | |
| 16 | Ryzhikov | Sergei Nikolaevich | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-27 | 08.04.2025 | 05:47:15.309 UTC | Soyuz MS-27 | 09.12.2025 | 05:03:33 UTC | 244d 23h 16m 18s | |
| 17 | Zubritsky | Aleksei Vitalyevich | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-27 | 08.04.2025 | 05:47:15.309 UTC | Soyuz MS-27 | 09.12.2025 | 05:03:33 UTC | 244d 23h 16m 18s | |
| 18 | Kim | Jonathan Yong "Jonny" | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-27 | 08.04.2025 | 05:47:15.309 UTC | Soyuz MS-27 | 09.12.2025 | 05:03:33 UTC | 244d 23h 16m 18s |
on March 07, 2025 the command changed to Aleksei Ovchinin
 |
Expedition Report
|
ISS Expedition 72 began with undocking of
Soyuz MS-25
on September 23, 2024 at 08:36:30
UTC. With docking of SpaceX Crew-9 on September 29, 2024 at 21:30 UTC Nicklaus Hague and Aleksandr Gorbunov became Flight Engineers of Expedition 72. SpaceX Crew-8 undocked from the International Space Station on October 23, 2024 at 21:05 UTC and landed the next day safely with Matthew Dominick, Michael Barratt, Jeanette Epps and Aleksandr Grebyonkin. In preparation for the arrival of NASA's SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission, four crew members aboard the International Space Station relocated the agency's SpaceX Crew-9 Dragon spacecraft to a different docking port on November 03, 2024. NASA astronauts Nicklaus Hague, Sunita Williams, and Barry Wilmore, as well as Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov, undocked the spacecraft from the forward-facing port of the station's Harmony module at 11:35:04 UTC and redocked to the module's space-facing port at 12:25:15 UTC. The relocation, supported by flight controllers at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston and the Mission Control team at SpaceX in Hawthorne, California, freed Harmony's forward-facing port for a Dragon cargo spacecraft mission scheduled to launch no earlier than November 04, 2024. On November 05, 2024 at 02:29:31 UTC unmanned freighter Dragon SpX-31 or CRS-31 filled with nearly 6,000 pounds (2,700 kilograms) of supplies, a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft on a Falcon 9 rocket lifted off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each resupply mission to the station delivers scientific investigations in the areas of biology and biotechnology, Earth and space science, physical sciences, and technology development and demonstrations. Cargo resupply from U.S. companies ensures a national capability to deliver scientific research to the space station, significantly increasing NASA's ability to conduct new investigations aboard humanity's laboratory in space. In addition to food, supplies, and equipment for the crew, Dragon will deliver several new experiments, including the Coronal Diagnostic Experiment, to examine solar wind and how it forms. Dragon also delivers Antarctic moss to observe the combined effects of cosmic radiation and microgravity on plants. Other investigations aboard include a device to test cold welding of metals in microgravity, and an investigation that studies how space impacts different materials. The spacecraft autonomously docked on November 05, 2024 at 14:52:11 UTC to the forward port of the space station's Harmony module. Unmanned freighter Progress MS-27 filled with 'junk' and used-up equipment undocked from Poisk module on November 19, 2024 at 12:57:27 UTC. The unmanned transporter re-entered the atmosphere a few hours later and burned up over the South Pacific. Progress MS-29 launched on November 21, 2024 at 12:22:23.197 UTC from Baikonur. The Progress MS-29 is designed to deliver 2,487 kg of cargo to the International Space Station, including 1,155 kg of apparatus and equipment for station systems, packaging for scientific experiments, clothing, food, medical and sanitary products for the crew of the 72nd space station-duration expedition, 869 kg Fuel to refuel the station, 420 kg of drinking water for astronauts and 43 kg of nitrogen to replenish the ISS atmosphere. The Progress MS-29 spacecraft docked to the space-facing port of the International Space Station's Poisk mini-research module on November 23, 2024 at 14:31:17 UTC. The Dragon SpX-31 or CRS-31 spacecraft undocked on December 16, 2024 at 16:05 UTC from the forward port of the space station's Harmony module and fired its thrusters to move a safe distance away from the station after receiving a command from ground controllers at SpaceX. After re-entering Earth's atmosphere, the spacecraft splashed down off the coast of Florida. Scientific hardware and samples returning to Earth include GISMOS (Genes in Space Molecular Operations and Sequencing), which successfully conducted in-orbit sequencing of microbial DNA from the space station water system, and marks the first real look at the microbial population of the water system. In addition, SpaceTED (Space Tissue Equivalent Dosimeter) returns to Earth after collecting data on crew radiation exposure and characterizes the space radiation environment. The dosimeter is a student-developed technology demonstration and effectively operated for 11 months on station - six months longer than intended because of its success. Additionally, two specimens printed with ESA's (European Space Agency) Metal 3D Printer, will go to researchers for post-processing and analysis. Researchers will compare the specimens printed in microgravity with those printed on Earth. The goal is to demonstrate the capability to perform metal deposition, or the layering of metals, in 3D under sustained microgravity conditions and manufacture test specimens. Researchers aim to understand the performance and limitations of the chosen technology and become familiar with crewed and remote operations of the instrument onboard a space habitat. Also returning on spacecraft is the International Space Art and Poetry Contest, which invited students and educators around the world to submit drawings, paintings, or poems. Winning art submissions were printed on station, photographed in the cupola, and will be returned to their creators on Earth. In addition, Plasmonic Bubbles researchers will observe high-speed video of bubble behavior in microgravity to understand fundamental processes that occur on a heated bubble surface. Results may improve understanding of how molecules are deposited on bubble surfaces and enhance detection methods for health care and environmental industries. On December 19, 2024 Aleksei Ovchinin and Ivan Vagner performed the first spacewalk during Expedition 72 (7h 17m). They installed SPIN-X1-MVN X-ray spectrometer outside the Zvezda module. The 51-kilogram instrument will periodically scan the night sky almost completely in the X-ray range. Scientists expect this to lead to a better understanding of black holes. The other tasks were to remove the "Test" and "Endurance" experiments, move the external control panel for the ERA manipulator to another location and discard the stacking with old boards using the manipulator. Due to time constraints, the control panel for the ERA manipulator arm could not be relocated during this operation. Nicklaus Hague and Sunita Williams performed the first US spacewalk in Expedition 72 on January 16, 2025 (6h 00m). They replaced a rate gyro assembly that helps provide orientation control for the station, installed patches to cover damaged areas of light filters for an X-ray telescope called NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer), and replaced a reflector device used for navigational data on one of the international docking adapters. Additionally, the pair checked access areas and connector tools that will be used for future maintenance work on the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer. The next spacewalk occurred on January 30, 2025 (5h 26m). Sunita Williams and Barry Wilmore were scheduled to remove a radio frequency group antenna assembly (RFG) from the station's truss, collect samples of surface material for analysis from the Destiny laboratory and the Quest airlock to see whether microorganisms may exist on the exterior of the orbital complex, and prepare a spare elbow joint for the Canadarm2 robotic arm in the event it is needed for a replacement. Due to technical problems not all tasks could be finished. Progress MS-28 cargo spacecraft undocked from the ISS Zvezda module at 20:17:33 UTC on February 25, 2025. The deorbit maneuver is scheduled for 23:25 UTC. The launch of the Soyuz-2.1a launch vehicle with the Progress MS-30 cargo ship occurred on February 27 at 21:24:27.328 UTC. The Progress MS-30 will carry 2,599 kg of cargo to the International Space Station, including 1,179 kg of equipment and hardware for the station's systems, kits for scientific experiments, clothing, food, medical and sanitary-hygienic supplies for the crew of the 72nd long-term expedition, 950 kg of fuel for refueling the station, 420 kg of drinking water for the cosmonauts, and 50 kg of nitrogen to replenish the ISS atmosphere. The cargo includes the new Orlan-MKS No. 6 spacesuit to support cosmonauts' spacewalks under the Russian program. The spacecraft also carries kits for carrying out the Aseptic, Biodegradation, Virtual, Cascade, Lazma, Mirage, Neuroimmunity and Photobioreactor experiments at the station. Progress MS-30 docked autonomously after a two-day in-orbit journey to the aft port Zvezda module on March 01, 2025 at 23:02:30 UTC. The Progress MS-30 spacecraft will remain docked to the space station for approximately six months before departing for re-entry into Earth's atmosphere to dispose of trash loaded by the crew. SpaceX Crew-10 docked to Harmony PMA-2 / IDA-F on March 16, 2025 at 04:04 UTC. The spacecraft was launched on March 14, 2025 at 23:03:48 UTC. With docking the for crew members became Flight Engineers of Expedition 72. SpaceX Crew-9 undocked from the International Space Station on March 18, 2025 at 05:05 UTC. Onboard the spacecraft were Nicklaus Hague, Aleksandr Gorbunov and the former CST-100 Boe-CFT (Starliner) astronauts Barry Wilmore and Sunita Williams. After delivering more than 8,200 pounds (3,720 kilograms) of supplies, scientific investigations, commercial products, hardware, and other cargo to the orbiting laboratory for NASA and its international partners, Northrop Grumman's uncrewed Cygnus spacecraft NG-21 (S.S. Richard "Dick" Scobee) departed the International Space Station on March 28, 2025 at 10:55 UTC. Flight controllers on the ground sent commands for the space station's SSRMS robotic arm to detach Cygnus from the Unity module's Earth-facing port, then maneuver the spacecraft into position for release. NASA astronaut Nichole Ayers monitored Cygnus' systems upon its departure from the space station. Cygnus - filled with trash packed by the station crew - will be commanded to deorbit on March 30, 2025 setting up a re-entry where the spacecraft will safely burn up in Earth's atmosphere. The Soyuz MS-27 spacecraft carrying Jonathan Kim, Sergei Ryzhikov, and Aleksei Zubritsky docked to the Prichal module at 08:57 UTC on April 08, 2025, following a three-hour, two-orbit journey to the space station. They launched at 05:47:15.039 UTC on April 08, 2025 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Finally, on April 19, 2025 the command changed from Russian cosmonaut Aleksei Ovchinin to Japanese astronaut Takuya Onishi. With undocking of Soyuz MS-26 on April 19, 2025 at 21:57 UTC the Expedition 72 concluded and the new Expedition 73 began. |
EVA data
| Name | Start | End | Duration | Mission | Airlock | Suit | |
| EVA | Ovchinin, Aleksei | 19.12.2024, 15:36 UTC | 19.12.2024, 22:53 UTC | 7h 17m | ISS-72 | ISS - Poisk | Orlan-MKS No. 5 |
| EVA | Vagner, Ivan | 19.12.2024, 15:36 UTC | 19.12.2024, 22:53 UTC | 7h 17m | ISS-72 | ISS - Poisk | Orlan-MKS No. 4 |
| EVA | Hague, Nicklaus | 16.01.2025, 13:01 UTC | 16.01.2025, 19:01 UTC | 6h 00m | ISS-72 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3013 |
| EVA | Williams, Sunita | 16.01.2025, 13:01 UTC | 16.01.2025, 19:01 UTC | 6h 00m | ISS-72 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3003 |
| EVA | Williams, Sunita | 30.01.2025, 12:43 UTC | 30.01.2025, 18:09 UTC | 5h 26m | ISS-72 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3003 |
| EVA | Wilmore, Barry | 30.01.2025, 12:43 UTC | 30.01.2025, 18:09 UTC | 5h 26m | ISS-72 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3013 |
Relocations of Manned Spacecrafts
| Spacecraft | from | Undocking | Time UTC | to | Redocking | Time UTC |
| SpaceX Crew-9 | ISS - Harmony PMA-2/IDA-F | 03.11.2024 | 11:35:04 | ISS - Harmony PMA-3/IDA-Z | 03.11.2024 | 12:25:15 |
Photos
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
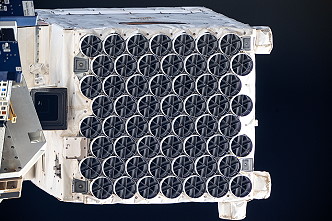 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Earth observation photos |
|
onboard photos |
|
more EVA photos |
|
| © |  |
Last update on January 07, 2026.  |
 |