Human Orbital Spaceflights
![]()
International Flight No. 131Soyuz TM-10VulkanUSSR |
 |
![]()
Launch, orbit and landing data
walkout photo |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
alternative crew photo |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
alternative crew photo |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
alternative crew photo |
Crew
| No. | Surname | Given names | Position | Flight No. | Duration | Orbits | |
| 1 | Manakov | Gennadi Mikhailovich | Commander | 1 | 130d 20h 35m 51s | 2070 | |
| 2 | Strekalov | Gennadi Mikhailovich | Flight Engineer | 4 | 130d 20h 35m 51s | 2070 |
Crew seating arrangement
|
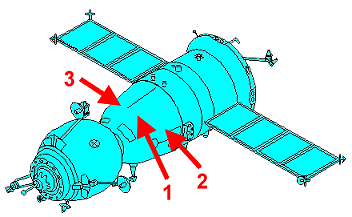 |
|
||||||||||||||||
Backup Crew
|
 |
|||||||||||||||
alternative crew photo |
Hardware
| Launch vehicle: | Soyuz-U2 (No. G15000-043) |
| Spacecraft: | Soyuz TM-10 (7K-STM No. 61?) |
Flight
|
Launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome and
landing 69 km northeast of Arkalyk. Following a two-day solo flight Soyuz TM-10 docked with the Mir space station on August 03, 1990. The cosmonauts became the seventh resident crew of Mir space station. The new crew arrived at Mir's aft port with four passengers - quail for cages in Kvant2. A quail laid an egg en route to the station. It was returned to Earth, along with 130 kg of experiment results and industrial products. The crew then set to work and linked Kristall's attitude control system to the Mir complex on August 28, 1990. On August 30, 1990 they practiced dealing with emergency situations which might arise in the expanded Mir complex. Between August 22, 1990 and September 11, 1990, Progress M-4 boosted the complex to a mean altitude of 390 km. Gennadi Strekalov and Gennadi Manakov installed a device for producing plasma on Progress M-4's docking unit before casting off the spacecraft on September 17, 1990. For three days it flew formation with the station, releasing plasma for the crew to observe and record. Progress M-5 arrived at the station on September 29, 1990. It carried television equipment for the upcoming joint Soviet-Japanese mission. It was also the first Progress-M equipped with a Raduga return capsule. On October 01, 1990 Soyuz TM-10's main engine pushed Mir to a mean altitude of 397 km. The KAP-350 and Priroda 5 cameras were used as part of the Makhichevan-90 Earth resources observation program, which studied the region between the Black and Caspian seas. Progress M-5 undocked on November 28, 1990 at 06:15:46 UTC. After deorbit burn, capsule separated for reentry with an expected landing in Kazakhstan at November 28, 1990 at 11:04:05 UTC. However, the recoverable capsule's beacon signal was never received after reentry. All experimental data and materials in the capsule were lost. Scientific work (astrophysical, geophysical, Earth observation, space materials science, biological and biotechnological research and experiments) was performed in the Soyuz TM-10-Kvant-Mir-Kvant2-Kristall complex. But they also had to do maintenance and repairing work. The only EVA in this mission was performed on October 29, 1990 (2h 45m). Gennadi Manakov and Gennadi Strekalov removed thermal insulation. They found that the hatch was beyond their ability to repair. They attached a device to the hatch to allow it to close properly. Soyuz TM-11 arrived at the station on December 04, 1990 with the Mir-8 relief crew of Viktor Afanasiyev, Musa Manarov (on his second Mir visit), and Japanese television journalist Toyohiro Akiyama. Toyohiro Akiyama's network, the Tokyo Broadcasting System (TBS), paid for the flight. The Soviets called this their first commercial spaceflight and claimed to have earned $14 million. The journalist was scheduled to make one 10-min TV broadcast and two 20-min radio broadcasts each day. Electrical power and video and TV system incompatibilities forced the Japanese to make extensive use of converters. His equipment, which weighed about 170 kg, was delivered by Progress-M spacecraft and set up in advance by Gennadi Manakov and Gennadi Strekalov. On December 05, 1990 Toyohiro Akiyama's couch was transferred to Soyuz TM-10. On December 08, 1990 Gennadi Manakov and Gennadi Strekalov commenced loading Soyuz TM-10's descent module with film and experiment results. TBS broadcast the landing of the Mir-7 crew together with Toyohiro Akiyama live from Kazakhstan. The Soyuz spacecraft is composed of three elements attached end-to-end - the Orbital Module, the Descent Module and the Instrumentation/Propulsion Module. The crew occupied the central element, the Descent Module. The other two modules are jettisoned prior to re-entry. They burn up in the atmosphere, so only the Descent Module returned to Earth. The deorbit burn lasted about 240 seconds. Having shed two-thirds of its mass, the Soyuz reached Entry Interface - a point 400,000 feet (121.9 kilometers) above the Earth, where friction due to the thickening atmosphere began to heat its outer surfaces. With only 23 minutes left before it lands on the grassy plains of central Asia, attention in the module turned to slowing its rate of descent. Eight minutes later, the spacecraft was streaking through the sky at a rate of 755 feet (230 meters) per second. Before it touched down, its speed slowed to only 5 feet (1.5 meter) per second, and it lands at an even lower speed than that. Several onboard features ensure that the vehicle and crew land safely and in relative comfort. Four parachutes, deployed 15 minutes before landing, dramatically slowed the vehicle's rate of descent. Two pilot parachutes were the first to be released, and a drogue chute attached to the second one followed immediately after. The drogue, measuring 24 square meters (258 square feet) in area, slowed the rate of descent from 755 feet (230 meters) per second to 262 feet (80 meters) per second. The main parachute was the last to emerge. It is the largest chute, with a surface area of 10,764 square feet (1,000 square meters). Its harnesses shifted the vehicle's attitude to a 30-degree angle relative to the ground, dissipating heat, and then shifted it again to a straight vertical descent prior to landing. The main chute slowed the Soyuz to a descent rate of only 24 feet (7.3 meters) per second, which is still too fast for a comfortable landing. One second before touchdown, two sets of three small engines on the bottom of the vehicle fired, slowing the vehicle to soften the landing. |
EVA data
| Name | Start | End | Duration | Mission | Airlock | Suit | |
| EVA | Strekalov, Gennadi | 29.10.1990, 21:45 UTC | 30.10.1990, 00:30 UTC | 2h 45m | Soyuz TM-10 | Mir - Kvant2 | Orlan-DMA No. 10 |
| EVA | Manakov, Gennadi | 29.10.1990, 21:45 UTC | 30.10.1990, 00:30 UTC | 2h 45m | Soyuz TM-10 | Mir - Kvant2 | Orlan-DMA No. 12 |
Graphics / Photos
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
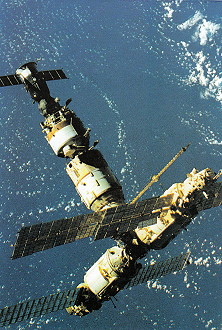 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| © |  |
Last update on March 28, 2020.  |
 |