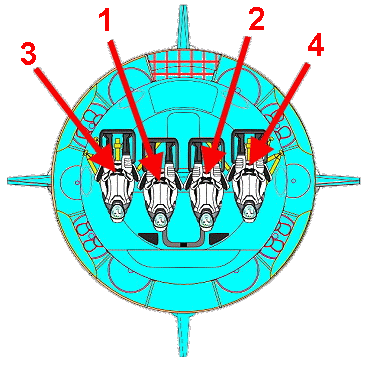
Launch from Cape Canaveral (
KSC), Launch
Complex 39-A at
NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The
Crew Dragon Endeavour docked 21 hours later with the
International Space Station. The spacecraft splashed down northeast of
Jacksonville in the Atlantic.
It was the
first all-private astronaut
mission to the International Space Station (
ISS) and a pivotal step toward Axiom Station, the
world's first commercial space station. The Axiom Space mission to the
International Space Station focused on science, education, and STEM outreach,
conducting more than 25 experiments, collecting critical data, and dedicating
more than 100 hours of human tended research during their 17-day mission.
Among the science experiments were:
TESSERAE (Tessellated
Electromagnetic Space Structures for the Exploration of Reconfigurable,
Adaptive Environments) is a multi-year research program exploring self-assembly
methods for in-space construction.
Using a human cancer stem cell
nano-bioreactor model (a vessel that accelerates cell growth conditions) and
cancer stem cell reporter system, this investigation will leverage the
accelerated aging aspects of the microgravity environment to evaluate early
pre-cancer and cancer changes in tumor organoids. This cellular biology project
is focused on identifying biomarkers for early detection and supports future
aims of cancer stem cell research on the
ISS. The Ax-1 crew will study cell samples under a
high-resolution microscope to determine cell cycle activity in cancer
growth.
The Japan Manned Space Systems Corporation (JAMSS) photocatalyst
air purification device was launched on Ax-1 for a technical demonstration to
verify the performance of the improved filter. This experiment also deployed a
control device without photocatalytic LEDs, to evaluate the JAMSS
photocatalytic filter. With an improved air filter, the JAMSS device was able
to clean the air on the ISS and remove cabin odor, using the power of light to
safely convert volatile compounds in the air into carbon dioxide and water with
the goal of improving the quality of life for living and working in space.
JAMSS was be the only Japanese company with research on the Ax-1
mission.
Translational Research Institute for Space Health (TRISH) is
conducting biomedical research on each of the crewmembers both before the
launch and after their return to Earth. A variety of data will be collected,
including physiological data, a battery of cognitive tests, balance and
perception tests, and visual acuity tests. Increasing human health and
performance is a goal of TRISH's EXPAND (Enhancing eXploration Platforms and
ANalog Definition) program, which compiles health data from private spaceflight
into a centralized research database and broadens understanding of how space
impacts human health and how to prepare humans for the demands of long-distance
and long-duration space travel, including to the Moon and eventually, to Mars.
![]()



![]()