Resident Crews of the International Space Station (ISS)
![]()
ISS: Expedition 51 |
 |
 |
 |
original crew photo |
alternative crew photo |
original crew photo |
|
original crew photo |
|
original crew photo |
|
original crew photo |
|
original crew photo |
|
original crew photo |
|
 |
 |
![]()
Crew, launch- and landing data
| No. | Nation | Surname | Given names | Position | Spacecraft (launch) |
Launch date |
Launch time |
Spacecraft (landing) |
Landing date |
Landing time |
Mission duration |
Orbits |
| 1 | Whitson | Peggy Annette | ISS-CDR | Soyuz MS-03 | 17.11.2016 | 20:20:13.099 UTC | Soyuz MS-03 | 03.09.2017 | 01:21:41.3 UTC | * 289d 05h 01m 29s | 4551 | |
| 2 | Yurchikhin | Fyodor Nikolayevich | Flight Engineer-1 | Soyuz MS-04 | 20.04.2017 | 07:13:43.171 UTC | Soyuz MS-04 | 03.09.2017 | 01:21:41.3 UTC | 135d 18h 07m 58s | 2112 | |
| 3 | Fischer | Jack David "2fish" | Flight Engineer-2 | Soyuz MS-04 | 20.04.2017 | 07:13:43.171 UTC | Soyuz MS-04 | 03.09.2017 | 01:21:41.3 UTC | 135d 18h 07m 58s | 2112 | |
| 4 | Novitsky | Oleg Viktorovich | Flight Engineer-4 | Soyuz MS-03 | 17.11.2016 | 20:20:13.099 UTC | Soyuz MS-03 | 02.06.2017 | 14:10:01 UTC | * 196d 17h 50m 18s | 3061 | |
| 5 | Pesquet | Thomas Gautier | Flight Engineer-5 | Soyuz MS-03 | 17.11.2016 | 20:20:13.099 UTC | Soyuz MS-04 | 02.06.2017 | 14:10:01 UTC | * 196d 17h 50m 18s | 3061 |
* including a leap second on December 31, 2016 at 23:59:60 UTC
unofficial Backup Crew
| No. | Nation | Surname | Given names | Position |
| 1 | Nespoli | Paolo Angelo | ISS-CDR | |
| 2 | Ryazansky | Sergei Nikolayevich | Flight Engineer | |
| 3 | Bresnik | Randolph James "Randy" | Flight Engineer | |
| 4 | Yurchikhin | Fyodor Nikolayevich | Flight Engineer | |
| 5 | Fischer | Jack David "2fish" | Flight Engineer |
 |
 |
 |
Expedition Report
|
ISS Expedition 51 began with the undocking of
spacecraft Soyuz
MS-02 on April 10, 2017 at 07:57:26
UTC. The former Expedition 50 (Shane
Kimbrough, Andrei
Borisenko and Sergei
Ryzhikov) returned safely to Earth. On April 15, 2017 the crew on the International Space Station (ISS) has successfully replaced a window pane on the Cupola module. The operation was conducted without any risk to the crew, thanks to the innovative design on the module's windows, which involves four panes allowing for internal replacement while risking no pressure loss for the Station. The Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services Cygnus OA-7 ("S.S. John Glenn") launched on April 18, 2017 at 15:11 UTC on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The spacecraft carried more than 7,500 pounds (3,400 kg) crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory to support the Expedition 51 and 52 crews. Cygnus consists of a pressurized cargo module for crew supplies, scientific experiments and equipment, together with an associated service module providing solar power and propulsion. Investigations onboard included an Advanced Plant Habitat, which will integrate new technology to increase overall efficiency, reliability, and robustness of plants grown on station. This experiment will build on the success of NASA's Veggie, the first fresh food growth system on station, and will provide ongoing research for the development of food production systems for long-duration exploration missions. Manipulating cell cultures in space is challenging as the cells can spontaneously grow in 3-D. Another new investigation bound for the U.S. National Laboratory will look at using magnetized cells and tools to make it easier to handle cells and cultures, and improve the reproducibility of experiments. The Slosh Coating experiment will investigate a special type of coating that can repel liquids when applied to container walls. If effective, the liquid repellent could be used to design more efficient storage tanks for propellant and other fluids used in space exploration. There also were a number of CubeSats onboard Cygnus that were deployed from the NanoRacks CubeSat Deployment on the space station, including a NASA science payload known as IceCube, which will provide data to scientists' understanding of ice clouds and their role in climate change. The International Space Station is a convergence of science, technology and human innovation that demonstrates new technologies and makes research breakthroughs not possible on Earth. The space station has been occupied continuously since November 2000. In that time, more than 200 people and a variety of international and commercial spacecraft have visited the orbiting laboratory. The space station remains the springboard to NASA's next great leap in exploration, including future missions to an asteroid and Mars. When Cygnus arrived to the space station on April 22, 2017, Peggy Whitson and Thomas Pesquet used the space station's robotic arm, Canadarm2, to take hold of the spacecraft. After Canadarm2 captured Cygnus (10:05 UTC), ground commands were sent for the station's arm to rotate and installed it on the bottom of the station's Unity module (12:39 UTC). Cygnus remained on the station until June 04 2017, when it departed with several tons of trash for a fiery reentry into Earth's atmosphere. Prior to re-entry, a third experiment to test was conducted to study how fire burns in space. Following a six hours solo flight Soyuz MS-04 docked to ISS on April 20, 2017. Fyodor Yurchikhin and Jack Fischer became the ISS Expedition 51 (together with ISS Expedition 50 crew members Oleg Novitsky, Thomas Pesquet and Peggy Whitson). With the arrival Expedition 51 became a five-person-crew. On April 27, 2017, an ISS reboost was performed using module Zvezda thrusters. This reboost was to set up for Soyuz MS-03 landing planned on June 02, 2017. The engines started at 05:10 UTC and fired 30 seconds. The ISS got 0.46 m/sec more speed. The actual parameters are 403.64 km x 426.8 km. The ISS needs 92.61 minutes for each orbit. The first spacewalk in Expedition 51 on May 12, 2017 (4h 13m) featured Peggy Whitson and Jack Fischer replacing an avionics box on the starboard truss called an ExPRESS Logistics Carrier (ELC), a storage platform. The ExPRESS Carrier Avionics, or ExPCA is located on the starboard 3 truss of the station on one of the depots housing critical spare parts. It was replaced with a unit delivered to the station in April 2017 aboard the Orbital ATK Cygnus cargo spacecraft. In addition, the astronauts installed a connector that will route data to the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer and help the crew determine the most efficient way to conduct future maintenance on cosmic ray detector. The astronauts also installed a protective shield on the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3, which was moved from the Tranquility to the Harmony module in March 2017. This adapter will host a new international docking port for the arrival of commercial crew spacecraft. Other tasks were cancelled due to technical problems. After a delay in beginning of this spacewalk due to the loss of a service and cooling umbilical (SCU) to a water leak there was not enough battery power for the more planned tasks. On May 17, 2017, an ISS reboost was performed using module Zvezda thrusters. This reboost was to set up for Soyuz MS-03 landing planned on June 02, 2017. The engines started at 22:15 UTC and fired 13 seconds. The ISS got 0.2 m/sec more speed. A contingency spacewalk by Peggy Whitson and Jack Fischer on May 23, 2017 (2h 46m) was needed. The astronauts replaced a backup multiplexer-demultiplexer (MDM) that failed on May 20, 2017. The box is one of the station's two external MDMs that provide commands to some of the space station's systems, including the external cooling system, solar alpha rotary joints (SARJ) and mobile transporter rail car. The multiplexer-demultiplexer (MDM) is 27 x 42 centimeters in diameter and has a mass of 23 kilograms. The failed relay box was installed in the space station truss March 30, 2017 during a spacewalk by Peggy Whitson and Shane Kimbrough. While Peggy Whitson replaced the MDM, Jack Fischer installed a pair of antennas on the U.S. Destiny Laboratory module to enhance wireless communication capability for future spacewalks. Finally, the station command changed from US astronaut Peggy Whitson to Russian cosmonaut Fyodor Yurchikhin. With undocking of Soyuz MS-03, carrying Oleg Novitsky and Thomas Pesquet, on June 02, 2017 at 10:47:04 UTC the Expedition 51 concluded and the new ISS Expedition 52 began. Peggy Whitson remained onboard the station for an extended stay. Among the US experiment are: Extremophiles Just as humans have maintained a constant presence aboard the space station since 2000, so have microorganisms. Because the facility isn't influenced by any other biological environment, only by entering and exiting crewmembers and supplies, the station is a special and unusual microbial habitat. Higher radiation, lower nutrient levels and a microgravity environment make the station an extreme biotope for microbes. Archaea and extremophilic bacteria have not been considered as a significant contributor to the microbiome that inhabits the ISS, although they constitute a significant part of the microbial communities that have been found in spacecraft assembly clean rooms. This investigation will test for the Archaea and extremophile bacteria by sampling locations within the interior of the space station over a period of approximately six months and comparing them against samples from spacecraft clean rooms and visiting vehicles. Eli Lilly Lypholization Lypholization, or freeze-drying, is used in in formulating pharmaceutical drugs, as well as preserving food and medications both on Earth and in space. The Eli-Lilly Lypholization investigation studies how this process occurs in a microgravity environment, and what improvements may be made to the current lypholization processes in the pharmaceutical industry, as well as other industries. Results from this investigation will improve our understanding of how foods, drugs and other compounds may be preserved in space, aiding in the planning of future, long duration spaceflight. Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass Cosmic rays reach Earth from far outside the solar system with energies well beyond what man-made accelerators can achieve. The Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass (CREAM) instrument, attached to the Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility, measures the charges of cosmic rays ranging from hydrogen to iron nuclei. The data collected from the CREAM instrument will be used to address fundamental science questions such as: Do supernovae supply the bulk of cosmic rays? What is the history of cosmic rays in the galaxy? Can the energy spectra of cosmic rays result from a single mechanism? Tested in several long duration balloon flights, the CREAM instrument holds the longest known exposure record for a single balloon-borne experiment at approximately 161 days of exposure. CREAM's three-year mission will help the scientific community to build a stronger understanding of the fundamental structure of the universe. During the stay on board of the ISS the crews of Expeditions 51 / 52 carried out the following scientific experiments (without Russian experiments): ACE-T-9 (Advanced Colloids Experiment ACE-T-9 Marr Imaging, Folding, and Assembly of Colloidal Molecules) ACME (Advanced Combustion Microgravity Experiment) ADCs in Microgravity (Efficacy and Metabolism of Azonafide Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) in Microgravity) AMS-02 (Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer - 02) ATOMIZATION (Detailed validation of the new atomization concept derived from drop tower experiments - Aimed at developing a turbulent atomization simulator) Aerosol Samplers (Aerosol Sampling Experiment) Aquapad (Aquapad) Area PADLES (Area Passive Dosimeter for Life-Science Experiments in Space) At Home in Space (Culture, Values, and Environmental Adaptation in Space) BASS-II (Burning and Suppression of Solids - II) BEAM (Bigelow Expandable Activity Module) BRIC-22 (Biological Research in Canisters-22) Biochem Profile (Biochemical Profile) Biomolecule Sequencer (Biomolecule Sequencer) Body Measures (Quantification of In-Flight Physical Changes - Anthropometry and Neutral Body Posture) Brain-DTI (Brain-DTI) CALET (CALorimetric Electron Telescope) CASIS PCG 6 (Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators) CAST (Crew Autonomous Scheduling Test) CATS (Cloud-Aerosol Transport System) CEO (Crew Earth Observations) CFE-2 (Capillary Flow Experiment - 2) CLYC-Crystal Growth (Crystal Growth of Cs2LiYCl6:Ce Scintillators in Microgravity) CREAM (Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass) Capillary Structures (Capillary Structures for Exploration Life Support) Cardio Ox (Defining the Relationship Between Biomarkers of Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress and the Risk for Atherosclerosis in Astronauts During and After Long-duration Spaceflight) Circadian Rhythms (Circadian Rhythms) Cool Flames Investigation (Cool Flames Investigation) DECLIC DSI-R (DEvice for the study of Critical LIquids and Crystallization - Directional Solidification Insert-Reflight) DECLIC HTI-R (DEvice for the study of Critical LIquids and Crystallization - High Temperature Insert-Reflight) DOSIS-3D (Dose Distribution Inside the International Space Station - 3D) Detached Melt and Vapor Growth of InI (Detached Melt and Vapor Growth of InI in SUBSA Hardware) Dose Tracker (Dose Tracker Application for Monitoring Medication Usage, Symptoms, and Adverse Effects During Missions) Dynamic Surf (Experimental Assessment of Dynamic Surface Deformation Effects in Transition to Oscillatory Thermo capillary Flow in Liquid Bridge of High Prandtl Number Fluid) ECHO (ECHO) EDOS-2 (Early Detection of Osteoporosis in Space-2) ESA-Active-Dosimeters (European Crew Personal Active Dosimeter) EVERYWEAR (EVERYWEAR) Energy (Astronaut's Energy Requirements for Long-Term Space Flight) ExHAM-CFRP Mirror (Space Environmental Testing of Lightweight and High-Precision Carbon Composite Mirrors) ExHAM-Solar Sail (Space Environment Exposure Tests of Functional Thin-Film Devices for Solar Sail) Exerc-Orthostatic Tolerance (Structured Exercise Training as Countermeasure to Space Flight-Induced Orthostatic Intolerance) FLUIDICS (Fluid Dynamics in Space) FNS (Fast Neutron Spectrometer) Fine Motor Skills (Effects of Long-Duration Microgravity on Fine Motor Skills: 1 year ISS Investigation) Fluid Shifts (Fluid Shifts Before, During and After Prolonged Space Flight and Their Association with Intracranial Pressure and Visual Impairment) Fruit Fly Lab -02 (FFL-02) (The effects of microgravity on cardiac function, structure and gene expression using the Drosophila model) Functional Immune (Functional Immune Alterations, Latent Herpesvirus Reactivation, Physiological Stress and Clinical Incidence Onboard the International Space Station) GRASP (Gravitational References for Sensimotor Performance: Reaching and Grasping) GRIP (Grip) Gecko Gripper (Gecko Gripper) Genes in Space-2 (Genes in Space-2) Group Combustion (Elucidation of Flame Spread and Group Combustion Excitation Mechanism of Randomly-distributed Droplet Clouds) HDEV (High Definition Earth Viewing) Habitability (Habitability Assessment of International Space Station) Honeywell-Morehead-DM-7 (Honeywell-Morehead-DM-7) IPVI (Non-invasive assessment of intracranial pressure for space flight and related visual impairment) ISS Ham Radio (ARISS) (International Space Station Ham Radio (also known as Amateur Radio on the International Space Station (ARISS))) ISS RapidScat (ISS-RapidScat) Immuno-2 (Immuno-2) In-flight Education Downlinks (International Space Station In-flight Education Downlinks) Intervertebral Disc Damage (Risk of Intervertebral Disc Damage after Prolonged Space Flight) JAXA ELF (Electrostatic Levitation Furnace (ELF)) JAXA Low Temp PCG (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Protein Crystallization Growth) JAXA PCG (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Protein Crystallization Growth) LDST (Long Duration Sorbent Testbed) LMM Biophysics 1 (The Effect of Macromolecular Transport of Microgravity Protein Crystallization) LMM Biophysics 3 (Growth Rate Dispersion as a Predictive Indicator for Biological Crystal Samples Where Quality Can be Improved with Microgravity Growth) Lighting Effects (Testing Solid State Lighting Countermeasures to Improve Circadian Adaptation, Sleep, and Performance During High Fidelity Analog and Flight Studies for the International Space Station) MAGVECTOR (MagVector) MATISS (MATISS) MAXI (Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image) MED-2 (Miniature Exercise Device) MOBIPV (Mobile Procedure Viewer) MSL SCA-Batch 2b-ESA (Material Science Lab Batch 2b) MSL SCA-GEDS-German (NASA Sample Cartridge Assembly) MUSCLE BIOPSY (Muscle Biopsy) MVIS Controller-1 (MVIS Controller-1) Made In Space Fiber Optics (Optical Fiber Production in Microgravity) Magnetic 3D Cell Culturing (Magnetic 3D Cell Culture for Biological Research in Microgravity) Maritime Awareness (Global AIS on Space Station (GLASS)) Marrow (The MARROW study (Bone Marrow Adipose Reaction: Red Or White?)) Medical Consumables Tracking (Medical Consumables Tracking) Meteor (Meteor Composition Determination) Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells (Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells) Miniaturized Particle Telescope (Miniaturized Particle Telescope) Multi-Omics (Multi-omics analysis of human microbial-metabolic cross-talk in the space ecosystem) Music and Space ( Music and Space) NICER (Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer) NanoRacks-CID (NanoRacks-CID) NanoRacks-KE IIM (NanoRacks-SMDC-Kestrel Eye IIM) NanoRacks-NDC-CCSJ-Beta-Amyloid Peptide (NanoRacks-NDC-Calumet College of St. Joseph-Beta-Amyloid Peptide) NeuroMapping (Spaceflight Effects on Neurocognitive Performance: Extent, Longevity, and Neural Bases) OsteoOmics (Gravitational Regulation of Osteoblast Genomics and Metabolism) PBRE (Packed Bed Reactor Experiment) PK-4 (Plasma Kristall-4) PS-TEPC (Establishment of dosimetric technique in the International Space Station (ISS) with Position Sensitive Tissue Equivalent Proportional Chamber) Passive Thermal Flight Experiment (Passive Thermal Flight Experiment) Phase Change HX (Phase Change Heat Exchanger Project) Probiotics (Study for evaluating the impact of continuous consumption of probiotics on immune function and intestinal microbiota in astronauts under closed microgravity environment) RED-Data2 (Thermal Protection Material Flight Test and Reentry Data Collection) RFID Logistics Awareness ( RFID-Enabled Autonomous Logistics Management (REALM)) ROSA (Roll-Out Solar Array) Radi-N2 (Radi-N2 Neutron Field Study) Radiation Environment Monitor (Radiation Environment Monitor) Repository (National Aeronautics and Space Administration Biological Specimen Repository) Robonaut (Robonaut) Rodent Research-5 (RR-5) (Systemic Therapy of NELL-1 for Osteoporosis) SAGE III-ISS (Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment III-ISS) SCAN Testbed (Space Communications and Navigation Testbed) SEDA-AP (Space Environment Data Acquisition Equipment - Attached Payload) SG100 Cloud Computer (SG100 Cloud Computing Payload) SPHERES-Slosh (SPHERES-Slosh) SPHERES-Zero-Robotics (Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites-Zero-Robotics) STP-H5 APS (Space Test Program-H5 Automated Plume Sentry) STP-H5 CSP (STP-H5-Center for High-performance REconfigurable Computing (CHREC) Space Processor) STP-H5 EHD (STP-H5-Electro-Hydro Dynamics) STP-H5 FPS (STP-H5-Fabry Perot Spectrometer for Methane) STP-H5 GROUP-C (Space Test Program-H5-GPS Radio Occultation and Ultraviolet Photometry Co-located) STP-H5 ICE (STP-H5-Innovative Coatings Experiment) STP-H5 LIS (STP-H5-Lightning Imaging Sensor) STP-H5 LITES (STP-H5-Limb-Imaging Ionospheric and Thermospheric Extreme-Ultraviolet Spectrographs) STP-H5 RHEME (STP-H5-Radiation Hardened Electronic Memory Experiment) STP-H5 Raven (Raven) STP-H5 SHM (STP-H5-Structural Health Monitoring) STP-H5 Space Cube - Mini (STP-H5-SpaceCube - Mini) STP-H5 iMESA-R (Space Test Program-H5-integrated Miniature Electro-Static Analyzer-Reflight) Saffire-III (Spacecraft Fire Experiment-III) Sally Ride EarthKAM (Sally Ride Earth Knowledge Acquired by Middle School Students) Sarcolab (Myotendinous and Neuromuscular Adaptation to Long-term Spaceflight) Seedling Growth-3 (Seedling Growth-3) Skinsuit (Operational and Technical Evaluation of Gravity Loading Countermeasure Skinsuit) Slosh Coating (Slosh Coating Experiment) Space Headaches (Space Headaches) Space Pup (Effect of space environment on mammalian reproduction) Sprint (Integrated Resistance and Aerobic Training Study) Stem Cells (Study on the Effect of Space Environment to Embryonic Stem Cells to Their Development) Story Time From Space (Story Time From Space) Straight Ahead in Microgravity (Straight Ahead in Microgravity) Strata-1 (Strata-1) TBone (Assessment of the effect of space flight on bone quality using three-dimensional high resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT)) Telescience Resource Kit (Flight Demonstration of Telescience Resource Kit) Telomeres (Assessing Telomere Lengths and Telomerase Activity in Astronauts) Tomatosphere-US (Tomatosphere-US) Two-Phase Flow (Interfacial behaviors and Heat transfer characteristics in Boiling Two-Phase Flow) UBNT (Ultrasonic Background Noise Test) Vascular Echo (Cardiac and Vessel Structure and Function with Long-Duration Space Flight and Recovery) Veg-03 (Veg-03) Vessel ID System (Vessel ID System) Water Monitoring Suite (Water Monitoring Suite) ZBOT (Zero Boil-Off Tank) |
EVA data
| Name | Start | End | Duration | Mission | Airlock | Suit | |
| EVA | Whitson, Peggy | 12.05.2017, 13:08 UTC | 12.05.2017, 17:21 UTC | 4h 13m | ISS-51 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3008 |
| EVA | Fischer, Jack | 12.05.2017, 13:08 UTC | 12.05.2017, 17:21 UTC | 4h 13m | ISS-51 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3006 |
| EVA | Whitson, Peggy | 23.05.2017, 11:20 UTC | 23.05.2017, 14:06 UTC | 2h 46m | ISS-51 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3008 |
| EVA | Fischer, Jack | 23.05.2017, 11:20 UTC | 23.05.2017, 14:06 UTC | 2h 46m | ISS-51 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3006 |
Photos / Graphics
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
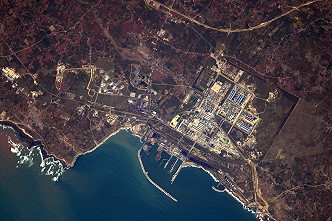 |
 |
 |
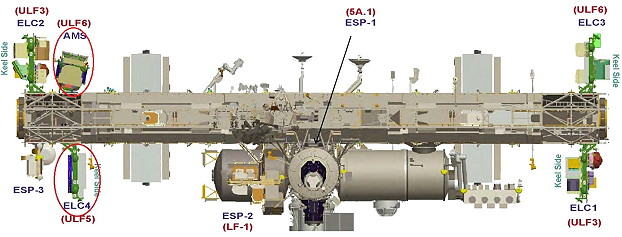 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
more Earth observation photos |
|
more EVA photos |
|
more onboard photos |
|
| © |  |
Last update on December 15, 2020.  |
 |