Resident Crews of the International Space Station (ISS)
![]()
ISS: Expedition 37 |
 |
 |
 |
alternative crew photo |
|
 |
 |
 |
![]()
Crew, launch- and landing data
| No. | Nation | Surname | Given names | Position | Spacecraft (launch) |
Launch date |
Launch time |
Spacecraft (landing) |
Landing date |
Landing time |
Mission duration |
Orbits |
| 1 | Yurchikhin | Fyodor Nikolayevich | ISS-CDR | Soyuz TMA-09M | 28.05.2013 | 20:31:24.262 UTC | Soyuz TMA-09M | 11.11.2013 | 02:49:00.1 UTC | 166d 06h 17m 36s | 2581 | |
| 2 | Kotov | Oleg Valeriyevich | Flight Engineer-1 | Soyuz TMA-10M | 25.09.2013 | 20:58:50.41 UTC | Soyuz TMA-10M | 11.03.2014 | 03:23:48.4 UTC | 166d 06h 24m 58s | 2580 | |
| 3 | Ryazansky | Sergei Nikolayevich | Flight Engineer-2 | Soyuz TMA-10M | 25.09.2013 | 20:58:50.41 UTC | Soyuz TMA-10M | 11.03.2014 | 03:23:48.4 UTC | 166d 06h 24m 58s | 2580 | |
| 4 | Hopkins | Michael Scott | Flight Engineer-3 | Soyuz TMA-10M | 25.09.2013 | 20:58:50.41 UTC | Soyuz TMA-10M | 11.03.2014 | 03:23:48.4 UTC | 166d 06h 24m 58s | 2580 | |
| 5 | Parmitano | Luca Salvo | Flight Engineer-5 | Soyuz TMA-09M | 28.05.2013 | 20:31:24.262 UTC | Soyuz TMA-09M | 11.11.2013 | 02:49:00.1 UTC | 166d 06h 17m 36s | 2581 | |
| 6 | Nyberg | Karen Lujean | Flight Engineer-6 | Soyuz TMA-09M | 28.05.2013 | 20:31:24.262 UTC | Soyuz TMA-09M | 11.11.2013 | 02:49:00.1 UTC | 166d 06h 17m 36s | 2581 |
unofficial Backup Crew
| No. | Nation | Surname | Given names | Position |
| 1 | Tyurin | Mikhail Vladislavovich | ISS-CDR | |
| 2 | Skvortsov | Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Jr. | Flight Engineer | |
| 3 | Artemyev | Oleg Germanovich | Flight Engineer | |
| 4 | Swanson | Steven Ray "Swanny" | Flight Engineer | |
| 5 | Mastracchio | Richard Alan "Rick" | Flight Engineer | |
| 6 | Wakata | Koichi | Flight Engineer |
 |
 |
 |
Expedition Report
|
Launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome (Oleg
Kotov,
Sergei
Ryazansky and Michael
Hopkins with
Soyuz
TMA-10M). Fyodor
Yurchikhin, Luca
Parmitano and Karen
Nyberg were onboard since May 29, 2013 (arrival with
Soyuz
TMA-09M). ISS Expedition 37 began with the undocking of spacecraft Soyuz TMA-08M on September 10, 2013 at 23:35:28 UTC. The former Expedition 36 (Pavel Vinogradov, Aleksandr Misurkin and Christopher Cassidy) returned safely to Earth. With the arrival of Soyuz TMA-10M on September 26, 2013 the Expedition 37 became a six-person-crew. Soyuz TMA-10M carried Oleg Kotov, Sergei Ryazansky and Michael Hopkins to the space station. On September 29, 2013 astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) used a robotic arm to capture and attach a Cygnus cargo resupply spacecraft, marking several spaceflight firsts for NASA and its partner, Orbital Sciences Corp. of Dulles, Va. The station's Expedition 37 crew reported the spacecraft - loaded with about 1,300 pounds (589 kilograms) of cargo - berthed at 12:44 UTC, following an 11-day journey to the orbiting laboratory. Orbital's Cygnus was launched on the company's Antares rocket on September 18, 2013 from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport Pad-0A at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. This was the first flight of a spacecraft to the space station from the state. After a series of tests designed to demonstrate Cygnus' ability to navigate, maneuver, lock on to the station and abort its approach, NASA cleared the spacecraft to approach the station Sunday morning. European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano and NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg captured Cygnus with the station's robotic arm, then attached the capsule on the bottom of the station's Harmony node, completing installation by bolting the Cygnus to Harmony. Cygnus had been scheduled for a rendezvous with the space station on September 22, 2013. Due to a data format mismatch, the first rendezvous attempt was postponed. Orbital updated and tested a software patch to fix the issue. Cygnus' arrival also was postponed pending the September 26, 2013 arrival of the Expedition 37 crew. The Canadarm2 released Orbital Sciences’ Cygnus commercial craft on October 22, 2013 after three weeks at the International Space Station. Flight Engineers Luca Parmitano and Karen Nyberg were at the controls of the robotics workstation removing Cygnus from the Harmony node then safely releasing it. On November 01, 2013 Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin and Flight Engineers Karen Nyberg and Luca Parmitano undocked their Soyuz TMA-09M spacecraft from the Rassvet module on the Earth-facing side of the station at 3:33 a.m. CDT (08:33 UTC). After backing the vehicle a safe distance away, Fyodor Yurchikhin rotated the Soyuz and began the flyaround to the rear of the station. Carefully aligning the spacecraft with the docking port on the aft end of the Zvezda service module, which was vacated by the European Space Agency's fourth Automated Transfer Vehicle on Monday, Fyodor Yurchikhin guided the spacecraft in for its docking at 3:54 a.m. CDT (08:54 UTC). Soyuz move sets the stage for the launch and arrival of a trio of new station crew members. The only spacewalk in this Expedition 37 was performed by Oleg Kotov and Sergei Ryazansky on November 09, 2013 (5h 50m). The cosmonauts carried the Olympic torch when they venture outside the International Space Station. After the photo opportunity, they prepared a pointing platform on the hull of the station's Zvezda service module for the installation of a high-resolution camera system in December 2013, relocate of a foot restraint for use on future spacewalks and deactivate an experiment package. The torch, an icon of international cooperation through sports competition, arrived at the space station Thursday aboard a Soyuz spacecraft carrying three crew members Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos, Richard Mastracchio of NASA and Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. It returned to Earth on November 11, 2013, aboard another Soyuz spacecraft vehicle along with crew members Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos, Karen Nyberg of NASA, and Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency. Expedition 37 included a variety of research, but several new investigations will focus on human health and human physiology. The crew also will perform experiments that cover technology demonstration, Earth and space science, and biology and biotechnology. The crew also will engage in educational activities. Eleven new experiments were designed by the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program. The Salivary Markers investigation involves the collection of blood, saliva, urine and a health assessment on six subjects preflight, in-flight and postflight to determine if immune system impairment caused by spaceflight increases the possibility for infection or poses a significant health risk to crewmembers aboard the International Space Station. The investigation is designed to determine the effects of long-term exposure to microgravity on a host of salivary antimicrobial proteins, hidden viruses that may reactivate, antibacterial properties of saliva, and blood markers associated with the cells and mechanisms that defend the immune system. Biochemical Profile: Blood and urine are commonly used to assess an astronaut's health as well as conduct research in physiological disciplines by measuring key physical characteristics in these fluids that may reflect illness or disease. In support of research studies, this project will collect, process and store blood and urine samples obtained during the preflight, in-flight and postflight phases of International Space Station missions and maintain a database of results from the analysis of these samples. This database will offer supporting evidence to scientists by providing metabolic profiles of the effects of spaceflight on human physiology. Body Measures: Currently, NASA does not have sufficient in-flight human body measurement data gathered to assess the impact of physical body shape and size changes on spacesuit sizing. This study will involve collecting body measurement data using digital still and video imagery and a tape measure to measure segmental length, height, depth, and circumference data for all body segments - chest, waist, hip, arms, legs, etc. - from astronauts for preflight, in-flight and postflight conditions. NanoRacks Experiments: Eleven experiments are from the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program, part of the National Center for Earth and Space Science Education. Student teams from across the United States designed their own experiments using flight approved fluids and materials. Research areas include antibacterial resistance, hydroponics, cellular division, combining substances with oxygen in microgravity, seed growth, photosynthesis and the food making process in microgravity. Finally, the station command changed from Russian cosmonaut Pavel Vinogradov to Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov. With undocking of Soyuz TMA-09M on November 10, 2013 at 23:26:31 UTC, carrying Fyodor Yurchikhin, Luca Parmitano and Karen Nyberg the Expedition 37 concluded and the new ISS Expedition 38 began. During the stay on board of the ISS the crews of Expeditions 37 / 38 carried out the following scientific experiments: 3DA1 Camcorder (Panasonic 3D Camera) ACE-1 (Advanced Colloids Experiment-1) AMO-TOCA (Autonomous Mission Operations TOCA Autonomous Operations Project) AMS-02 (Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer - 02) APEX-02-1 (Advanced Plant EXperiments 02-1) ATOMIZATION (Detailed validation of the new atomization concept derived from drop tower experiments--Aimed at developing a turbulent atomization simulator) Amine Swingbed (Amine Swingbed) Aniso Tubule (Roles of cortical microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins in gravity-induced growth modification of plant stems) Area PADLES (Area Passive Dosimeter for Life-Science Experiments in Space) BCAT-3-4-CP (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 3 and 4: Critical Point) BCAT-4-Poly (Binodal Colloidal Aggregation Test - 4: Polydispersion) BCAT-5-3D-Melt (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 5: Three-Dimensional Melt) BCAT-5-Compete (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 5: Compete) BCAT-5-PhaseSep (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test-5: Phase Separation) BCAT-5-Seeded Growth (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 5: Seeded Growth) BCAT-6-Colloidal Disks (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 6 - Colloidal Disks) BCAT-6-PS-DNA (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 6: Polystyrene - Deoxyribonucleic Acid) BCAT-6-Phase Separation (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 6 - Phase Separation) BCAT-6-Seeded Growth (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - 6: Seeded Growth) BCAT-C1 (Binary Colloidal Alloy Test - C1) BP Reg (A Simple In-flight Method to Test the Risk of Fainting on Return to Earth After Long-Duration Space Flights) Biochemical Profile (NASA Biochemical Profile Project) Biological Rhythms 48hrs (The effect of long-term microgravity exposure on cardiac autonomic function by analyzing 48-hours electrocardiogram) Biotube-MICRO (Biotube-Magnetophoretically Induced Curvature in Roots) Bisphosphonates (Bisphosphonates as a Countermeasure to Space Flight Induced Bone Loss) Body Measures (Quantification of In-Flight Physical Changes - Anthropometry and Neutral Body Posture) CARTILAGE (CARTILAGE) CCF (Capillary Channel Flow) CEO (Crew Earth Observations) CFE-2 (Capillary Flow Experiment - 2) CPCG-HM (Commercial Protein Crystal Growth - High density protein crystal growth Modified) Cardio Ox (Defining the Relation Between Biomarkers of Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress and Atherosclerosis Risk in Astronauts During and After Long-duration Spaceflight) Circadian Rhythms (Circadian Rhythms) Comm Delay Assessment (Assessing the Impact of Communication Delay on Behavioral Health and Performance: An Examination of Autonomous Operations Utilizing the International Space Station) DECLIC DSI-R (DEvice for the study of Critical LIquids and Crystallization - Directional Solidification Insert-Reflight) DECLIC HTI-R (DEvice for the study of Critical LIquids and Crystallization - High Temperature Insert-Reflight) DOD SPHERES-RINGS (Department of Defense Synchronized Position, Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites-RINGS) DOSIS-3D (Dose Distribution Inside the International Space Station - 3D) DTN (Disruption Tolerant Networking for Space Operations) Dynamic Surf (Experimental Assessment of Dynamic Surface Deformation Effects in Transition to Oscillatory Thermo capillary Flow in Liquid Bridge of High Prandtl Number Fluid) EPO-Demos (Education Payload Operation - Demonstrations) ESA-EPO-PARMITANO (European Space Agency-Education Payload Operations-PARMITANO) Energy (Astronaut's Energy Requirements for Long-Term Space Flight) ExHam (Astrobiology Exposure and Micrometeoroid Capture Experiments) FASES (Fundamental and Applied Studies of Emulsion Stability) FASTER (Facility for Absorption and Surface Tension) FLEX-2 (Flame Extinguishment Experiment - 2) Functional Task Test (Physiological Factors Contributing to Postflight Changes in Functional Performance) Gravi-2 (Threshold Acceleration for Gravisensing - 2) HDEV (High Definition Earth Viewing) HREP-HICO (HICO and RAIDS Experiment Payload - Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean) HREP-RAIDS (HICO and RAIDS Experiment Payload - Remote Atmospheric and Ionospheric Detection System (RAIDS)) HiMassSEE (Spacecraft Single Event Environments at High Shielding Mass) Hip QCT (Feasibility Study: QCT Modality for Risk Surveillance of Bone - Effects of In-flight Countermeasures on Sub-regions of the Hip Bone.) Hyperspectral Imaging (Hyperspectral Imaging) ICE-GA (Italian Combustion Experiment for Green Air) ISERV (ISS SERVIR Environmental Research and Visualization System) ISS Ham Radio (International Space Station Ham Radio) ISS High Efficiency Particle Filter Analysis (International Space Station High Efficiency Particle Filter Analysis) ISS Medical Monitoring (International Space Station Medical Monitoring) InSPACE-3 (Investigating the Structure of Paramagnetic Aggregates from Colloidal Emulsions - 3) Intervertebral Disc Damage (Risk of Intervertebral Disc Damage after Prolonged Space Flight) JAXA PCG (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Protein Crystal Growth) JAXA-Commercial (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency - Commercial Payload Program) Journals (Behavioral Issues Associated with isolation and Confinement: Review and Analysis of Astronaut Journals) MAXI (Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image) MCE (Multi-mission Consolidated Equipment) MICAST-2 (The Microstructure Formation in Casting of Technical Alloys under Diffusive and Magnetically Controlled Convective Conditions-2) MISSE-8 (Materials International Space Station Experiment - 8) Manual Control (Assessment of Operator Proficiency Following Long-Duration Space Flight) Micro-5 (Investigation of host-pathogen interactions, conserved cellular responses, and countermeasure efficacy during spaceflight using the human surrogate model Caenorhabditis elegans) Microbe-A1 (On-board Microorganism Monitoring in Spacecrafts) Microbiome (Study of the Impact of Long-Term Space Travel on the Astronauts' Microbiome) Multi-Gas Monitor (Multi-Gas Monitor) OPALS (Optical PAyload for Lasercomm Science) Ocular Health (Prospective Observational Study of Ocular Health in ISS Crews) Pro K (Dietary Intake Can Predict and Protect Against Changes in Bone Metabolism during Spaceflight and Recovery) RRM (Robotic Refueling Mission) RRM-P2 (Robotic Refueling Mission Phase 2) Radi-N2 (Radi-N2 Neutron Field Study) Radiation Environment Monitor (Radiation Environment Monitor) Reaction Self Test (Psychomotor Vigilance Self Test on the International Space Station) Repository (National Aeronautics and Space Administration Biological Specimen Repository) Resist Tubule (Mechanisms of Gravity Resistance in Plants From Signal Transformation and Transduction to Response) Reversible Figures (Perspective Reversible Figures in Microgravity) Robonaut (Robonaut) SATS-Interact (Supervision of Autonomous and Teleoperated Satellites - Interact) SCAN Testbed (Space Communications and Navigation Testbed) SEDA-AP (Space Environment Data Acquisition Equipment - Attached Payload) SMILES (Superconducting Submillimeter-Wave Limb-Emission Sounder) SNFM (Serial Network Flow Monitor) SPHERES-Slosh (SPHERES-Slosh) SPHERES-Zero-Robotics (Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites-Zero-Robotics) STP-H4-ATT (Space Test Program-Houston 4-Active Thermal Tile) STP-H4-FireStation (Space Test Program-Houston 4-FireStation) STP-H4-GLADIS (Space Test Program - Houston 4 - Global Awareness Data-Exfiltration International Satellite) STP-H4-ISE 2.0 (Space Test Program-Houston 4-ISS SpaceCube Experiment 2.0) Salivary Markers (The Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Microgravity on Salivary Markers of Innate Immunity) Sally Ride EarthKAM (Sally Ride Earth Knowledge Acquired by Middle School Students) Sarcolab (Myotendinous and Neuromuscular Adaptation to Long-termSpaceflight) Seedling Growth-1 (Seedling Growth-1) Skin-B (Skin-B) Solar-SOLACES (Sun Monitoring on the External Payload Facility of Columbus - SOLar Auto-Calibrating EUV/UV Spectrophotometers) Solar-SOLSPEC (Sun Monitoring on the External Payload Facility of Columbus -Sun Monitoring on the External Payload Facility of Columbus -SOLar SPECtral Irradiance Measurements) Space Headaches (Space Headaches) Space Pup (Effect of space environment on mammalian reproduction) SpaceDRUMS (Space Dynamically Responding Ultrasonic Matrix System) Spinal Ultrasound (Sonographic Astronaut Vertebral Examination) Sprint (Integrated Resistance and Aerobic Training Study) T-Cell Act in Aging (T-Cell Activation in Aging) TEM (Transport Environment Monitor Packages) UBNT (Ultrasonic Background Noise Test) V-C REFLEX (Plastic alteration of vestibulo-cardiovascular reflex and its countermeasure) VIABLE ISS (eValuatIon And monitoring of microBiofiLms insidE International Space Station) Vascular (Cardiovascular Health Consequences of Long-Duration Space Flight) Vessel ID System (Vessel ID System) Windows on Earth (Windows on Earth). |
EVA data
| Name | Start | End | Duration | Mission | Airlock | Suit | |
| EVA | Ryazansky, Sergei | 09.11.2013, 14:34 UTC | 09.11.2013, 20:24 UTC | 5h 50m | ISS-37 | ISS - Pirs | Orlan-MK No. 4 |
| EVA | Kotov, Oleg | 09.11.2013, 14:34 UTC | 09.11.2013, 20:24 UTC | 5h 50m | ISS-37 | ISS - Pirs | Orlan-MK No. 5 |
Relocations of Manned Spacecrafts
| Spacecraft | from | Undocking | Time UTC | to | Redocking | Time UTC |
| Soyuz TMA-09M | ISS - Rassvet | 01.11.2013 | 08:33:25 | ISS - Zvezda | 01.11.2013 | 08:54:27 |
ISS Assembly
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Photos
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
more EVA photos |
|
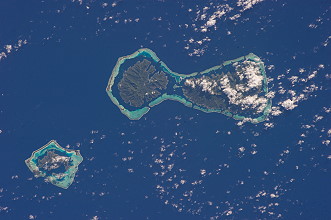
more Earth observation photos |
|
more onboard photos |
|
| © |  |
Last update on December 14, 2020.  |
 |